10 min read
Google Workspace Device Policy: What You Need to Know
If you're running a business and using Google Workspace, it’s important to have a device policy in place. Google Workspace Device Policy helps...
7 min read
![]() Promevo
|
Published: August 7, 2023
| Last Updated: April 23, 2025
Promevo
|
Published: August 7, 2023
| Last Updated: April 23, 2025
Email security is a major concern for today's business organizations. One effective method for protecting against spoofing, phishing, and spam is Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC).
When it comes to Google Workspace, implementing DMARC is crucial for maintaining a secure email environment. Let's take a closer look at DMARC and why it's so important for Google Workspace.
DMARC provides extra protection for email accounts by utilizing two other authentication methods: Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM).
SPF allows domain owners to authorize IP addresses that are allowed to send email for the domain, while DKIM adds a digital signature to each sent message for verification purposes.
With DMARC, receiving mail servers can check if messages meet the authentication requirements specified in the DMARC policy record. This ensures that messages appearing to come from an organization are authentic and have not been forged or altered during transit.
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that helps prevent email fraud, spoofing, and phishing. It allows domain owners to specify what actions should be taken when a message fails authentication checks or doesn't meet the specified DMARC policy.
By implementing DMARC, organizations can protect their domain reputation, enhance email deliverability, and reduce the risk of malicious activity originating from their domain.
Spoofing and phishing are common techniques used by attackers to deceive recipients and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. Spoofed messages appear to come from legitimate organizations or well-known entities, while phishing emails trick individuals into divulging confidential data.
DMARC plays a crucial role in combating these threats by providing email administrators with information about authentication issues and potential malicious activities originating from their domain.
DMARC not only strengthens security but also enhances email deliverability. By implementing DMARC policies and ensuring that outgoing messages pass authentication checks, organizations can improve their email reputation.
Receiving mail servers recognize authenticated messages and are more likely to deliver them to recipients' inboxes instead of marking them as spam. This helps organizations maintain reliable and efficient communication channels, ensuring that their legitimate messages reach the intended recipients.
DMARC helps email administrators prevent hackers and attackers from impersonating their organization or domain.
By implementing DMARC, you can authenticate your email messages and request reports from receiving email servers, which assist in identifying authentication issues and malicious activities associated with messages sent from your domain.
To configure DMARC for Google Workspace, it's important to set up DKIM and SPF first, as these authentication methods are used in conjunction with DMARC. DKIM adds a digital signature to each sent message, verifying its authenticity, while SPF authorizes IP addresses allowed to send emails on behalf of the domain.
Once DKIM and SPF are set up and have been authenticating messages for at least 48 hours, you can proceed to configure DMARC.
Start with a relaxed DMARC policy by creating a DMARC record with enforcement set to "none" and an email address configured to receive daily DMARC reports. This allows you to monitor email flow and collect data without the risk of rejecting or marking messages as spam. For example, you can set the DMARC policy as follows:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@solarmora.com
Review the daily DMARC reports to ensure that messages from your domain are sent by authorized servers and pass authentication checks. Analyze the reports to identify servers or services that fail DMARC and investigate any trends or issues, such as messages ending up in spam folders or bounce/error messages.
You can define DMARC functionality by entering a DMARC record in your domain's DNS settings. To add your DMARC record in Google Workspace, follow these steps:
To validate your DMARC setup, review the reports you receive daily. These reports provide valuable information about servers or third-party senders that are sending emails on behalf of your domain and the percentage of messages that pass or fail DMARC checks.
By analyzing the reports, you can identify any unauthorized or suspicious activities associated with your domain's email traffic.
Analyzing DMARC reports allows you to gain insights into your email ecosystem and detect potential issues. Look for patterns or trends that indicate problems, such as legitimate messages ending up in spam folders or messages failing DMARC authentication.
These insights can help you improve your email delivery and security, ensuring that only authorized servers send messages on behalf of your domain.
Implementing a DMARC policy in Google Workspace can significantly enhance your organization's email security. Here are some best practices to consider when setting up your DMARC policy.
When configuring your DMARC policy, it's important to choose the appropriate level of enforcement.
Google recommends starting with a relaxed policy to monitor email flow before gradually increasing the level of enforcement. Begin with a "none" policy, which only monitors email without rejecting or marking messages as spam. This allows you to receive reports and assess the authenticity of emails sent from your domain.
To implement a relaxed DMARC policy, update the DMARC DNS TXT record at your domain provider with the following parameters:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@solarmora.com
This policy applies to 100% of messages but has enforcement set to none, ensuring normal message delivery even if they don't pass DMARC authentication. The daily reports will provide valuable insights into your mail streams.
For effective email authentication, DMARC should be used in conjunction with SPF and DKIM. Before configuring DMARC, ensure that SPF and DKIM are properly set up and authenticating messages for at least 48 hours. This period allows sufficient time for SPF and DKIM to propagate and start validating email.
Once your DMARC policy is in place, regular monitoring is crucial to identify any issues and ensure the effective authentication of messages. Review the DMARC reports received daily to gain insights into the servers or third-party senders sending mail for your domain and the percentage of messages that pass or fail DMARC.
Pay attention to any trends indicating problems, such as legitimate messages ending up in spam folders or bounce/error messages. These insights will help you refine your email security measures and maintain the integrity of your domain's email communication.
DMARC ensures that incoming emails are thoroughly authenticated, reducing the risk of unauthorized senders impersonating your organization.
With proper monitoring and management of DMARC reports, you can identify and address potential security threats promptly, maintaining a secure email environment for your organization.
Remember to regularly review and update your DMARC policy as your organization's needs evolve to ensure optimal email security and protection against malicious activities.
If you're interested in using Google Workspace for your business, trust Promevo. We help you harness the robust capabilities of Google to accelerate the growth of your company and give you the momentum you need to achieve your most ambitious business goals.
With our expert consultation, comprehensive support, and exceptional service from end-to-end, you can drive maximum collaboration and productivity in your organization.
Yes, Google Workspace does support DMARC. By configuring DMARC records in the domain's DNS settings, administrators can enhance the security of their organization's email communication within Google Workspace.
To determine if DMARC is enabled in Google Workspace, you need to check the DNS settings of your domain and verify the presence of a DMARC record. Follow these steps to check if DMARC is enabled:
Please note that configuring DMARC requires prior setup DKIM and SPF, and they should be authenticating messages for at least 48 hours before enabling DMARC.
A DMARC TXT record is a DNS record that specifies how email servers handle and authenticate messages sent from a particular domain. It adds an additional layer of security to prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks.
The DMARC TXT record contains information such as the email policy for handling messages (e.g., "none" for no strict actions, "quarantine" for marking suspicious messages, or "reject" for blocking unauthorized messages), the email address to receive aggregate reports about email activity, and the percentage of messages to be subjected to DMARC validation.
To set up DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) for Google Workspace, you'll first need to have access to your domain's DNS settings. Here's the step-by-step process to set up DMARC:
Setting up DMARC helps protect your domain's email reputation and prevent email spoofing. It also allows you to receive reports on email authentication failures.
To add SPF and DKIM records to Google Workspace, you need to access your domain's DNS settings. Here are the steps to follow:
After these steps, Google Workspace will be able to authenticate your domain's outgoing emails using SPF and DKIM, which enhances email deliverability and helps prevent spoofing and spam.
DMARC policy not enabled in Google Workspace means your organization's email domain does not have Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance authentication turned on. DMARC works by aligning SPF and DKIM email authentication to prevent spoofing, phishing, and other malicious email from being sent from your domain.
Without a DMARC policy enabled, your domain is more vulnerable to impersonation attacks. Enabling DMARC provides additional security by telling receiving servers to reject or quarantine emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks. This protects your users from forged emails claiming to come from your domain.
Enabling DMARC policy in Workspace provides powerful email validation and gives you visibility into messages from your domain. Turning on DMARC policy hardens security and prevents misuse of your organizational emails.
Meet the Author
Promevo is a Google Premier Partner for Google Workspace, Google Cloud, and Google Chrome, specializing in helping businesses harness the power of Google and the opportunities of AI. From technical support and implementation to expert consulting and custom solutions like gPanel, we empower organizations to optimize operations and accelerate growth in the AI era.

10 min read
If you're running a business and using Google Workspace, it’s important to have a device policy in place. Google Workspace Device Policy helps...
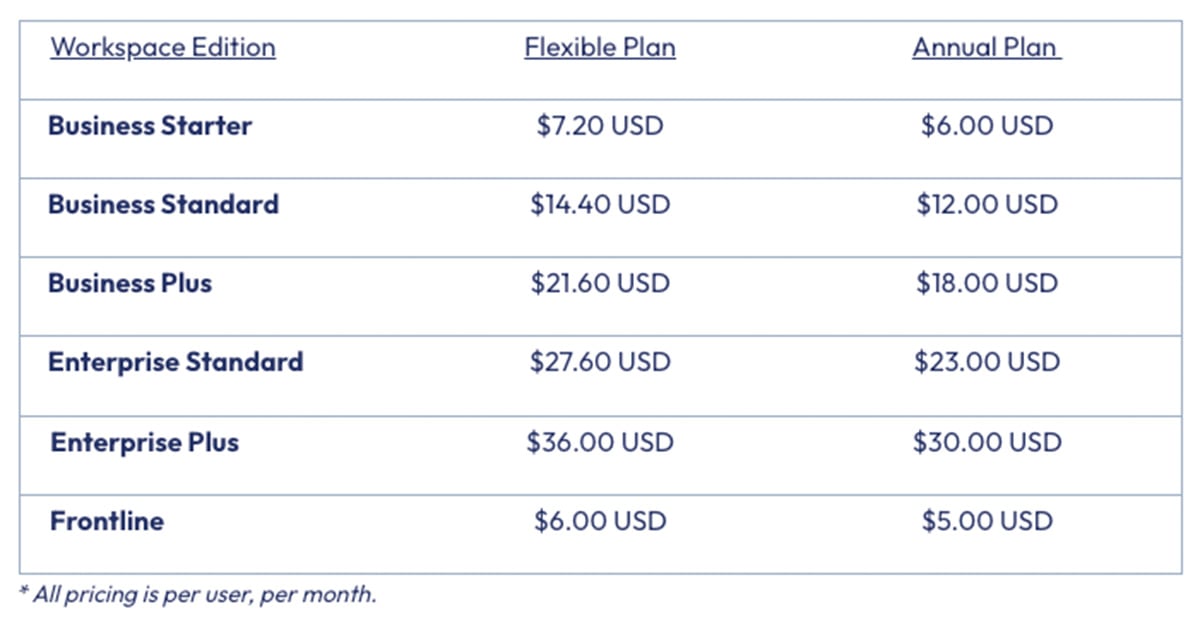
8 min read
Google Workspace recently announced pricing updates with additional flexible and commitment payment options to provide customers with more options....

6 min read
Are you looking to streamline your business operations and maximize efficiency in your Google Workspace environment? It's time to take control of...